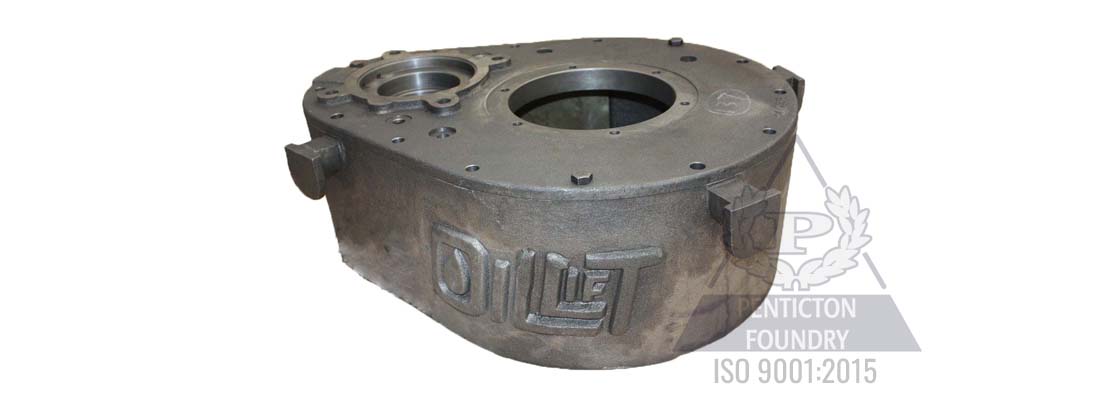
ASTM A536 refers to the standard specification for ductile iron castings. Ductile iron is also called spheroidal graphite iron or nodular iron. In contrast to gray iron, where the graphite occurs as a network of flakes, the graphite in ductile iron occurs as spheroids. This confers a number of advantages on ductile iron.
Ductile iron, depending on grade, offers different properties. A536 Grade 60-40-18, for example, possesses maximum ductility, excellent machinability and low temperature toughness. A536 Grade 120-90-02, on the other hand, possesses very high strength and wear resistance (though not as wear resistant as our chrome white irons). If your application requires moderate ductility and impact resistance, coupled with high strength, you may want to consider ASTM A536 Grade 80–55–06. ASTM A536 Grade 65-45-12 is the workhorse of the ductile iron family, and the alloy most designers will select when converting a mild steel fabrication to a ductile iron casting. Its tensile and yield strength is very close to that of mild steel. Of the fully pearlitic grades of ductile iron, A536 Grade 100-70-03 is our most commonly poured alloy. A skilled foundry can, through alloying alone, achieve this grade for most castings.
Our ductile iron castings are produced to meet the ASTM A536 standard. This ensures that our customers obtain the engineered properties required for their specific application. All of our castings are created using the latest heat treatment/chemistry design and controls.
We produce several grades of ductile iron, including:
We also pour austempered ductile iron and ASTM A439 Grade D2 58-30-8.
Possible Ductile Iron Applications
- Frames
- Gear Boxes
- Cable Drums
- Pumps
Contact one of our sales representatives today to discuss your specific application and the alloy you require.